Professor Sanjay Sinha
Cardiovascular diseases
Email: ss661@cam.ac.uk
Laboratory: Cambridge Stem Cell Institute, Jeffrey Cheah Biomedical Centre
Departmental Affiliation: Medicine
Biography
Sanjay Sinha is a British Heart Foundation (BHF) Senior Research Fellow and a Professor in Cardiovascular Regenerative Medicine at the University of Cambridge. He completed medical training in Cambridge, followed by cardiology clinical training and a PhD in Manchester. Dr Sinha then carried out post-doctoral studies in the USA with Prof Gary Owens on smooth muscle biology before establishing an independent group at Cambridge. He is also a Consultant in Cardiology and he combines his research work with clinical duties at Addenbrooke’s Hospital, Cambridge, where he treats patients with a wide variety of cardiovascular diseases.
Funding
British Heart Foundation, Wellcome, Stroke Association
External Links
Research
My lab's overall aim is to develop new treatments for vascular diseases, in particular those involving vascular smooth muscle cells (SMC), using a stem cell based approach.
We have pioneered the generation of embryonic lineage-specific vascular SMC, through the lateral mesoderm, paraxial mesoderm, neural crest and epicardium, from human embryonic stem cells (hESC) and induced pluripotent stem cells, using chemically defined conditions. We have utilised this system to model genetically triggered aortopathies, such as Marfan and Loeys-Dietz syndromes. These "disease-in-a-dish" models are being used to understand the pathobiology of these conditions and to screen for new treatments.
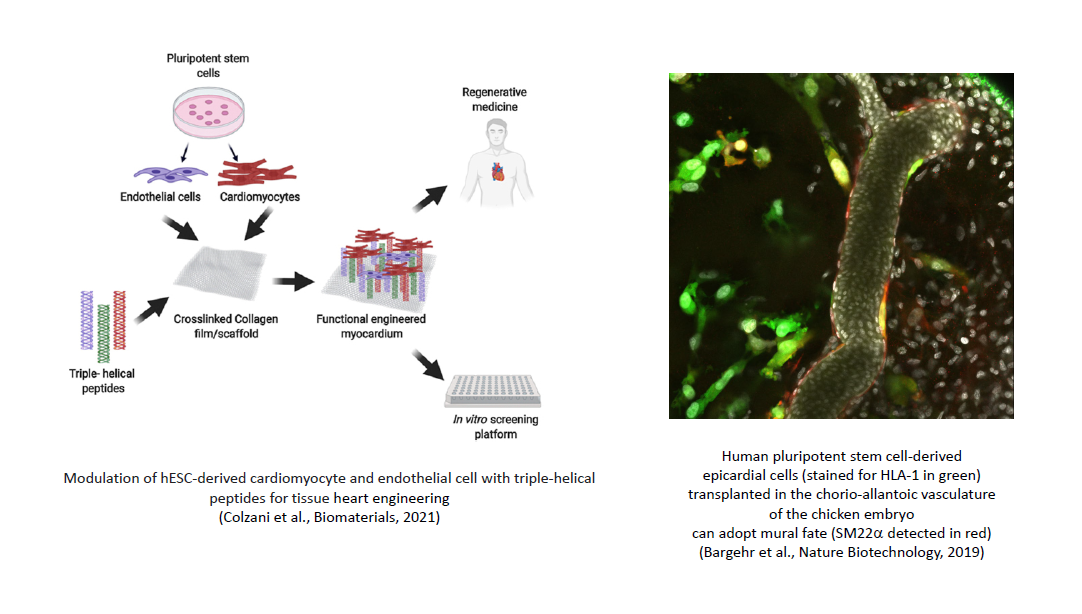
Additionally we are testing the regenerative potential of hESC-derived epicardium and other cardiovascular cell types for heart repair after myocardial infarction, either through direct injection or in the form of an in vitro generated myocardial "patch".
Sinha Group photo 2023
Plain English
Blood vessel diseases cause heart attacks, strokes and aortic aneurysms (a ballooning then tearing of the main artery in the body). We use human stem cells to generate smooth muscle cells, one of the main cell types that make up the blood vessel wall. If we use skin cells from patients with vascular diseases to make stem cells then the smooth muscle cells from those (induced) stem cells will have the same abnormalities as in the patient, thus providing a way to generate a "disease-in-a-dish". With these and other approaches we are trying to understand how blood vessels become diseased and trying to find new treatments for these diseases. We are also developing ways to transplant our stem cell generated cells to reverse the damage caused by a heart attack.
Key Publications
- Colzani M, Malcor JD, Hunter EJ, Bayraktar S, Polkinghorne M, Krieg T, Cameron R, Best S, Farndale RW, Sinha S. Modulating hESC-derived cardiomyocyte and endothelial cell function with triple-helical peptides for heart tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2020 Dec 16;269:120612. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33385684. PMCID: PMC7884910
- Gambardella L, McManus S, Moignard V, Sebukhan D, Delaune A, Andrews S, Bernard WG, Morrison M, Riley PR, Göttgens B, Le Novère N and Sinha S. BNC1 regulates epicardial heterogeneity and function. Development 2019;146: dev174441 (Epub) doi: 10.1242/dev.174441: PMID: 31767620
- Bargehr J, Ong LP, Colzani M, Davaapil H, Hofsteen P, Bhandari S, Gambardella L, Le Novère N, Iyer D, Sampaziotis F, Weinberger F, Bertero A, Leonard A, Bernard WG, Martinson A, Figg N, Regnier M, Bennett M, Murry CE, and Sinha S. Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Epicardial Cells Augment Cardiomyocyte-Driven Heart Regeneration. Nature Biotech 2019;37:895-906. PMID: 31375810
- Granata A, Serrano F, Bernard WG, McNamara M, Low L, Sastry P, and Sinha S. An iPSC-derived vascular model of Marfan syndrome identifies key mediators of smooth muscle cell death. Nature Genetics, 2017;49:97-109
- Iyer D, Gambardella L, Bernard W, Serrano F, Mascetti VL, Pedersen RA, Talasila A, Sinha S. Robust Derivation of Epicardium and Its Differentiated SMC progeny from Human PSCs. Development 2015;142:1528-41. PMCID:PMC4392600
- Cheung C, Bernardo AS, Trotter MW, Pedersen RA, Sinha S. Generation of human vascular SMC subtypes provides insights into embryological origin-dependent disease susceptibility. Nature Biotech 2012;30:165-73. PMCID:PMC3272383